Teaching Penetration Testing
Date:
Talk at Lancaster University, Lancaster, UK
At a Lancaster University education event, I presented work that I have been undertaking to improve the delivery of SCC.442 Penetration Testing.
There were three main problems that had been encountered in previous years:
- Students had unclear expectations in terms of what was expected from them
- Students struggled to approach technical problems in assessments
- Manual construction of lab and assessment material was time-consuming and unreliable
Issue 1 - Addressing Expectations
To identify clear expectations, the Revised Blooms Taxonomy has been mapped to the Cyber Kill Chain to provide details on what is expected from students at different levels of attainment.
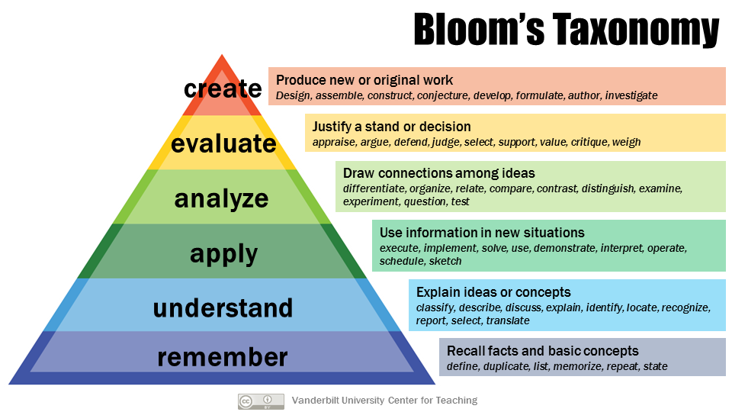
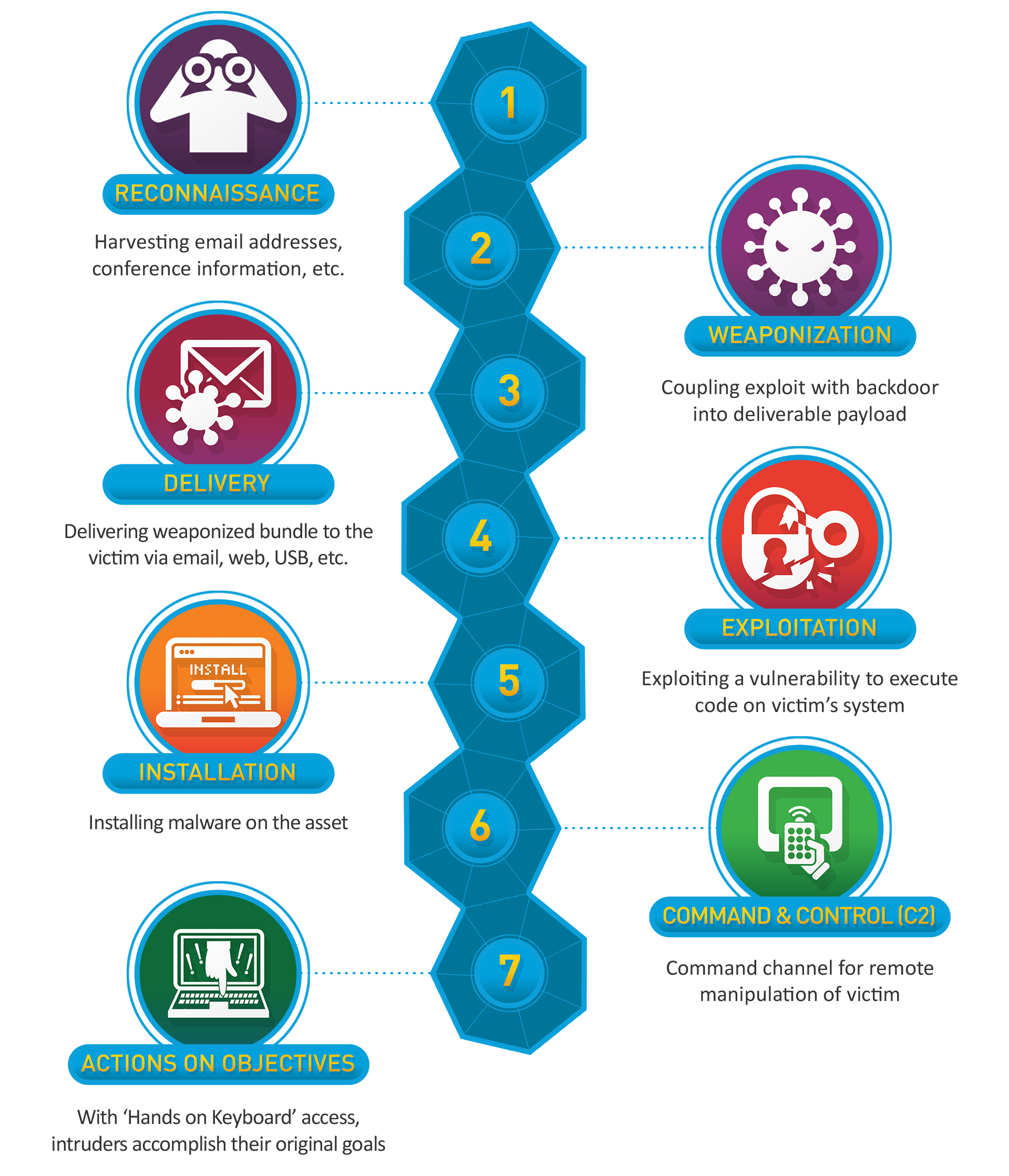
| Reconnaissance | Weaponization | Delivery | Exploitation | Installation | C&C | Act | |
| Remember | Know what the different commands and tools do. | ||||||
| Understand | Understand what configuration to run the different commands and tools with. | ||||||
| Apply | Ability to execute commands and run tools. | ||||||
| Analyse | Attributing recon. to services | Identify the types and versions of system and software | Identify how a payload or exploit should be delivered | Processing output from exploit | Determine if malware install is needed | What new actions can possibly be performed? | Determine next steps to achieve goal |
| Parse nmap scan and understand output | Parse nmap scan to identify services & versions | Use webserver to deploy reverse shell | Examine output from SQL injection | Analyse if msfvenom should be used | Identify if elevate privilege is possible | Identify how to elevate privilege | |
| Evaluate | Testing recon. result | Identify vulns. of system or software | Did the delivery succed? | Did the exploit succed? | Did the installation succed? | Can new actions be performed? | Decide which steps are most effective |
| Test recon. by opening browser on port 80 | Search databases for vulns. | Check if file transfer succeeded | Check if exploit succeeded | Check if reverse shell was successful | Consider pivoting | Consider best approach to pivot | |
| Create | Planning next steps based on recon. | Build malware or design exploit | Deliver malware or exploit | Produce an outcome from the malware or exploit | Malware installed or exploit usable | Obtained controllable system | Achieve objectives |
| Decide to perform privilege elevation | Built reverse shell using msfvenom | Reverse shell delivered to target | Exploit target to elevate privilege | Reverse shell installed on target | Connect reverse shell to Metasploit | Capture the flag |
Issue 2 - Approach to Problem Solving
An issue encountered in the past is that students treat lab exercises as a set of instructions to compromise a system. When applying these instructions during assessment, they end up failing to exploit the system due to its configuration being different. So students need to be presented with content that clearly encourages them to think about why they are taking certain actions.
- Encourage a scientific approach where students start a lab with a hypothesis and then reflect on this hypothesis at the end of the labs.
- Prompt students to consider why they are taking specific actions.
- Provide context as to why certain actions are appropriate.
- Start with large amounts of guidance and then reduce the guidance over time.
- Ensure students are exposed to appropriate sources throughout the labs, such as NVD, CWE, and CAPEC.
